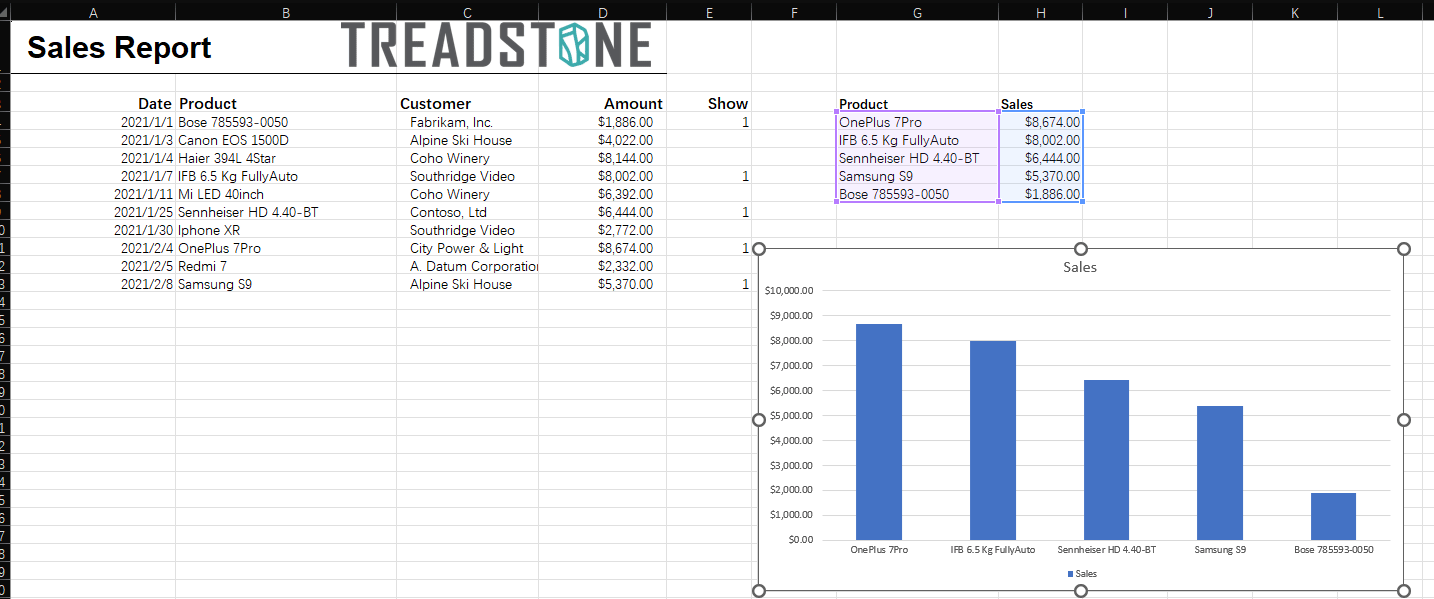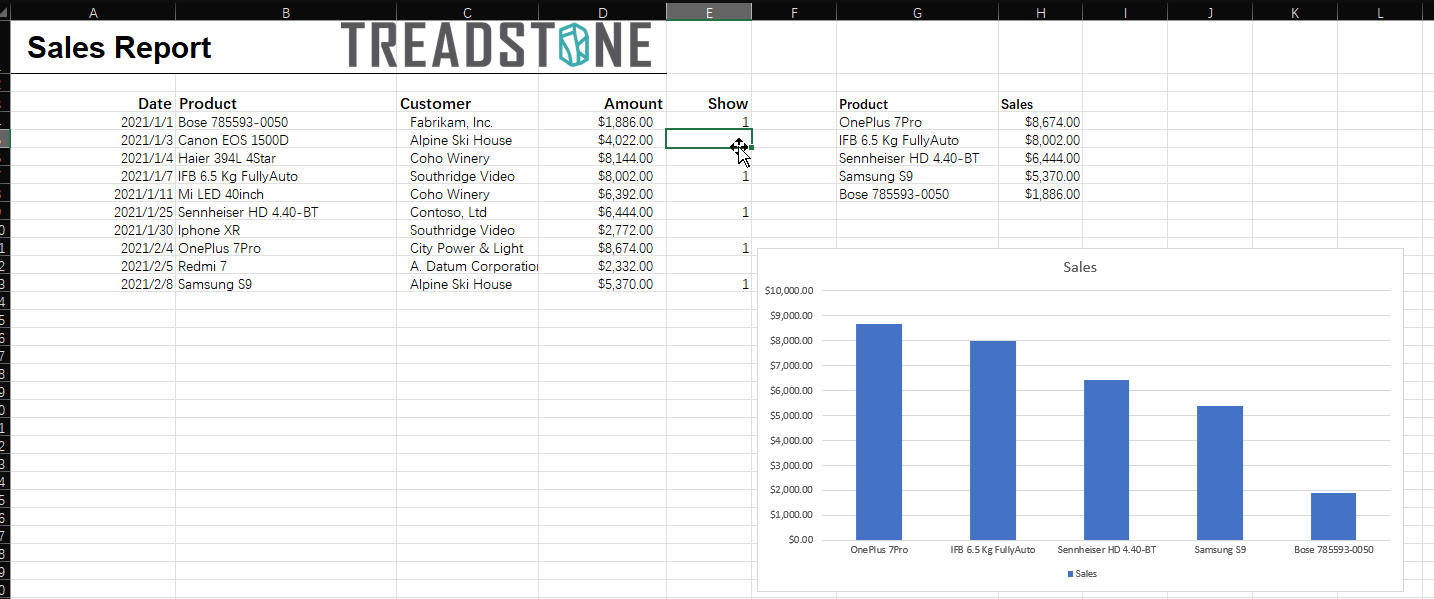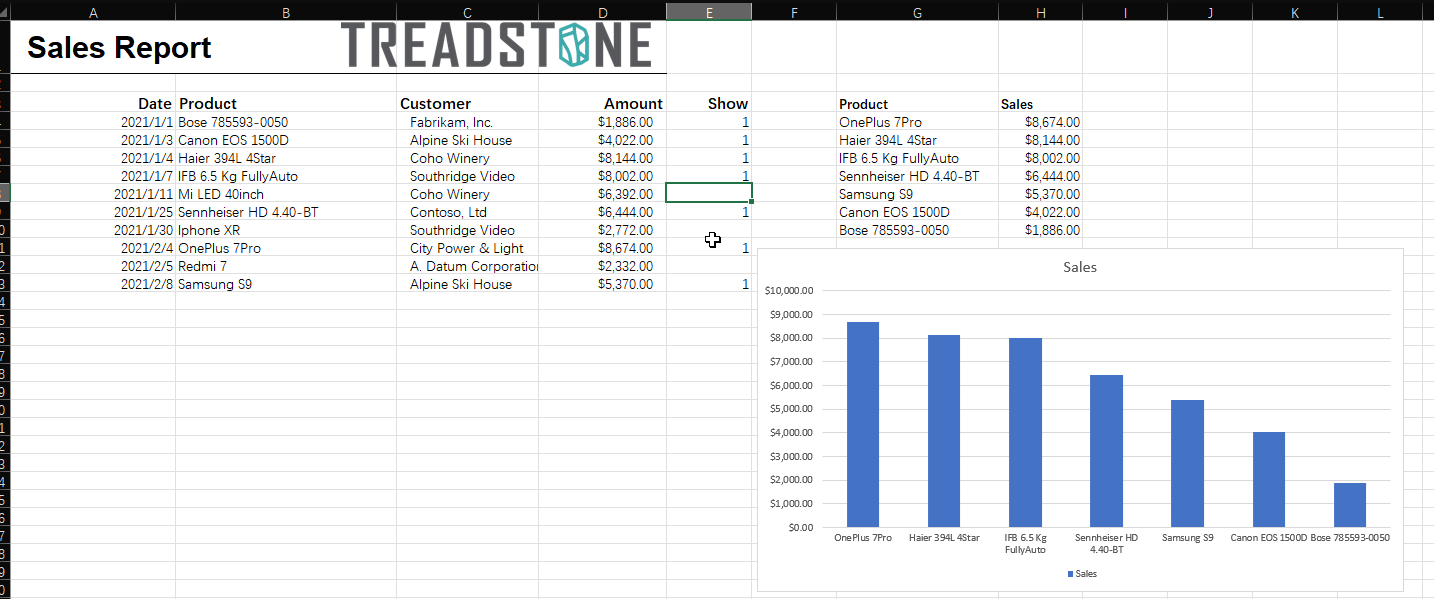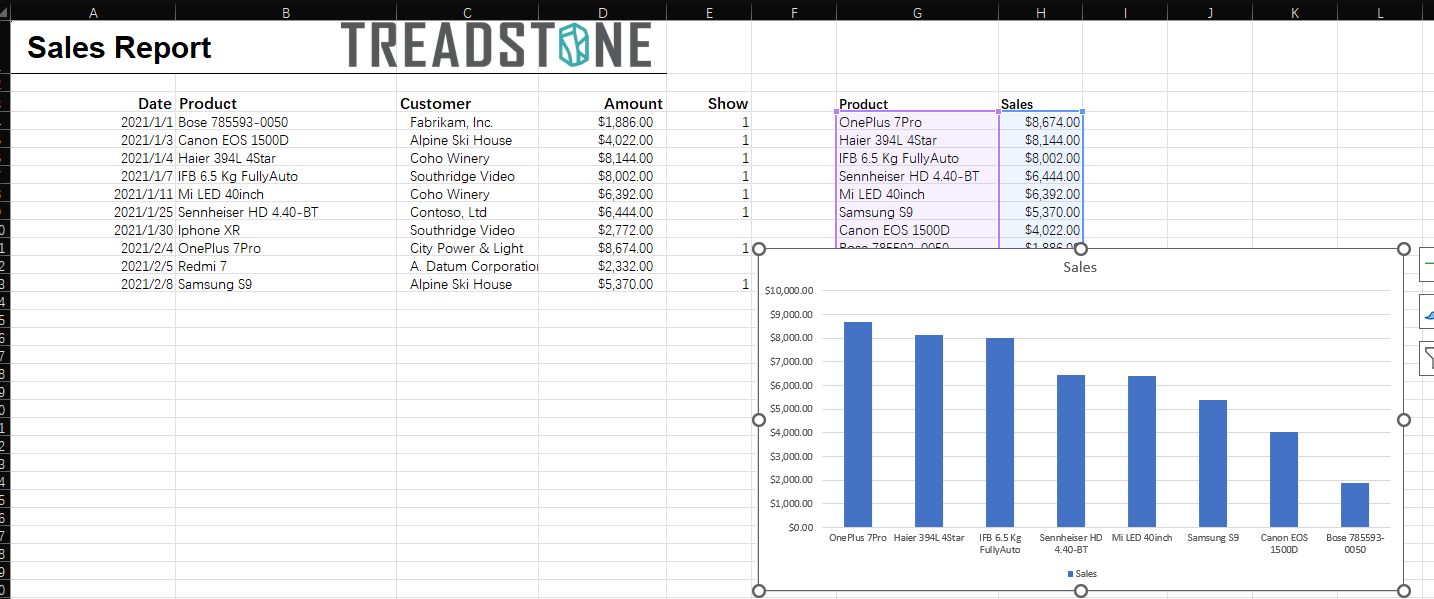
文章目录
- 结构体定义
- 操作函数
- 支持的AVOutputFormat
通过上面的分析,基本可以看到ffmpeg的套路了,首先一个context上下文,上下文里面一个priv_data 指针,然后再插件结构体中有一个priv_data_size,然后回调函数。
结构体定义
首先肯定是AVFormatContext,这个就是上下文,这个结构体太庞大了。特别要注意里面的AVIOContext,这两个回调可以从自己的内存中读取数据。另外还有一个AVStream的结构体,专门用来存储流。
/**
* Format I/O context.
* New fields can be added to the end with minor version bumps.
* Removal, reordering and changes to existing fields require a major
* version bump.
* sizeof(AVFormatContext) must not be used outside libav*, use
* avformat_alloc_context() to create an AVFormatContext.
*
* Fields can be accessed through AVOptions (av_opt*),
* the name string used matches the associated command line parameter name and
* can be found in libavformat/options_table.h.
* The AVOption/command line parameter names differ in some cases from the C
* structure field names for historic reasons or brevity.
*/
typedef struct AVFormatContext {
/**
* A class for logging and @ref avoptions. Set by avformat_alloc_context().
* Exports (de)muxer private options if they exist.
*/
const AVClass *av_class;
/**
* The input container format.
*
* Demuxing only, set by avformat_open_input().
*/
const struct AVInputFormat *iformat;
/**
* The output container format.
*
* Muxing only, must be set by the caller before avformat_write_header().
*/
const struct AVOutputFormat *oformat;
/**
* Format private data. This is an AVOptions-enabled struct
* if and only if iformat/oformat.priv_class is not NULL.
*
* - muxing: set by avformat_write_header()
* - demuxing: set by avformat_open_input()
*/
void *priv_data;
/**
* I/O context.
*
* - demuxing: either set by the user before avformat_open_input() (then
* the user must close it manually) or set by avformat_open_input().
* - muxing: set by the user before avformat_write_header(). The caller must
* take care of closing / freeing the IO context.
*
* Do NOT set this field if AVFMT_NOFILE flag is set in
* iformat/oformat.flags. In such a case, the (de)muxer will handle
* I/O in some other way and this field will be NULL.
*/
AVIOContext *pb;
/* stream info */
/**
* Flags signalling stream properties. A combination of AVFMTCTX_*.
* Set by libavformat.
*/
int ctx_flags;
/**
* Number of elements in AVFormatContext.streams.
*
* Set by avformat_new_stream(), must not be modified by any other code.
*/
unsigned int nb_streams;
/**
* A list of all streams in the file. New streams are created with
* avformat_new_stream().
*
* - demuxing: streams are created by libavformat in avformat_open_input().
* If AVFMTCTX_NOHEADER is set in ctx_flags, then new streams may also
* appear in av_read_frame().
* - muxing: streams are created by the user before avformat_write_header().
*
* Freed by libavformat in avformat_free_context().
*/
AVStream **streams;
/**
* input or output URL. Unlike the old filename field, this field has no
* length restriction.
*
* - demuxing: set by avformat_open_input(), initialized to an empty
* string if url parameter was NULL in avformat_open_input().
* - muxing: may be set by the caller before calling avformat_write_header()
* (or avformat_init_output() if that is called first) to a string
* which is freeable by av_free(). Set to an empty string if it
* was NULL in avformat_init_output().
*
* Freed by libavformat in avformat_free_context().
*/
char *url;
/**
* Position of the first frame of the component, in
* AV_TIME_BASE fractional seconds. NEVER set this value directly:
* It is deduced from the AVStream values.
*
* Demuxing only, set by libavformat.
*/
int64_t start_time;
/**
* Duration of the stream, in AV_TIME_BASE fractional
* seconds. Only set this value if you know none of the individual stream
* durations and also do not set any of them. This is deduced from the
* AVStream values if not set.
*
* Demuxing only, set by libavformat.
*/
int64_t duration;
/**
* Total stream bitrate in bit/s, 0 if not
* available. Never set it directly if the file_size and the
* duration are known as FFmpeg can compute it automatically.
*/
int64_t bit_rate;
unsigned int packet_size;
int max_delay;
/**
* Flags modifying the (de)muxer behaviour. A combination of AVFMT_FLAG_*.
* Set by the user before avformat_open_input() / avformat_write_header().
*/
int flags;
#define AVFMT_FLAG_GENPTS 0x0001 ///< Generate missing pts even if it requires parsing future frames.
#define AVFMT_FLAG_IGNIDX 0x0002 ///< Ignore index.
#define AVFMT_FLAG_NONBLOCK 0x0004 ///< Do not block when reading packets from input.
#define AVFMT_FLAG_IGNDTS 0x0008 ///< Ignore DTS on frames that contain both DTS & PTS
#define AVFMT_FLAG_NOFILLIN 0x0010 ///< Do not infer any values from other values, just return what is stored in the container
#define AVFMT_FLAG_NOPARSE 0x0020 ///< Do not use AVParsers, you also must set AVFMT_FLAG_NOFILLIN as the fillin code works on frames and no parsing -> no frames. Also seeking to frames can not work if parsing to find frame boundaries has been disabled
#define AVFMT_FLAG_NOBUFFER 0x0040 ///< Do not buffer frames when possible
#define AVFMT_FLAG_CUSTOM_IO 0x0080 ///< The caller has supplied a custom AVIOContext, don't avio_close() it.
#define AVFMT_FLAG_DISCARD_CORRUPT 0x0100 ///< Discard frames marked corrupted
#define AVFMT_FLAG_FLUSH_PACKETS 0x0200 ///< Flush the AVIOContext every packet.
/**
* When muxing, try to avoid writing any random/volatile data to the output.
* This includes any random IDs, real-time timestamps/dates, muxer version, etc.
*
* This flag is mainly intended for testing.
*/
#define AVFMT_FLAG_BITEXACT 0x0400
#define AVFMT_FLAG_SORT_DTS 0x10000 ///< try to interleave outputted packets by dts (using this flag can slow demuxing down)
#if FF_API_LAVF_PRIV_OPT
#define AVFMT_FLAG_PRIV_OPT 0x20000 ///< Enable use of private options by delaying codec open (deprecated, does nothing)
#endif
#define AVFMT_FLAG_FAST_SEEK 0x80000 ///< Enable fast, but inaccurate seeks for some formats
#define AVFMT_FLAG_SHORTEST 0x100000 ///< Stop muxing when the shortest stream stops.
#define AVFMT_FLAG_AUTO_BSF 0x200000 ///< Add bitstream filters as requested by the muxer
/**
* Maximum number of bytes read from input in order to determine stream
* properties. Used when reading the global header and in
* avformat_find_stream_info().
*
* Demuxing only, set by the caller before avformat_open_input().
*
* @note this is \e not used for determining the \ref AVInputFormat
* "input format"
* @sa format_probesize
*/
int64_t probesize;
/**
* Maximum duration (in AV_TIME_BASE units) of the data read
* from input in avformat_find_stream_info().
* Demuxing only, set by the caller before avformat_find_stream_info().
* Can be set to 0 to let avformat choose using a heuristic.
*/
int64_t max_analyze_duration;
const uint8_t *key;
int keylen;
unsigned int nb_programs;
AVProgram **programs;
/**
* Forced video codec_id.
* Demuxing: Set by user.
*/
enum AVCodecID video_codec_id;
/**
* Forced audio codec_id.
* Demuxing: Set by user.
*/
enum AVCodecID audio_codec_id;
/**
* Forced subtitle codec_id.
* Demuxing: Set by user.
*/
enum AVCodecID subtitle_codec_id;
/**
* Maximum amount of memory in bytes to use for the index of each stream.
* If the index exceeds this size, entries will be discarded as
* needed to maintain a smaller size. This can lead to slower or less
* accurate seeking (depends on demuxer).
* Demuxers for which a full in-memory index is mandatory will ignore
* this.
* - muxing: unused
* - demuxing: set by user
*/
unsigned int max_index_size;
/**
* Maximum amount of memory in bytes to use for buffering frames
* obtained from realtime capture devices.
*/
unsigned int max_picture_buffer;
/**
* Number of chapters in AVChapter array.
* When muxing, chapters are normally written in the file header,
* so nb_chapters should normally be initialized before write_header
* is called. Some muxers (e.g. mov and mkv) can also write chapters
* in the trailer. To write chapters in the trailer, nb_chapters
* must be zero when write_header is called and non-zero when
* write_trailer is called.
* - muxing: set by user
* - demuxing: set by libavformat
*/
unsigned int nb_chapters;
AVChapter **chapters;
/**
* Metadata that applies to the whole file.
*
* - demuxing: set by libavformat in avformat_open_input()
* - muxing: may be set by the caller before avformat_write_header()
*
* Freed by libavformat in avformat_free_context().
*/
AVDictionary *metadata;
/**
* Start time of the stream in real world time, in microseconds
* since the Unix epoch (00:00 1st January 1970). That is, pts=0 in the
* stream was captured at this real world time.
* - muxing: Set by the caller before avformat_write_header(). If set to
* either 0 or AV_NOPTS_VALUE, then the current wall-time will
* be used.
* - demuxing: Set by libavformat. AV_NOPTS_VALUE if unknown. Note that
* the value may become known after some number of frames
* have been received.
*/
int64_t start_time_realtime;
/**
* The number of frames used for determining the framerate in
* avformat_find_stream_info().
* Demuxing only, set by the caller before avformat_find_stream_info().
*/
int fps_probe_size;
/**
* Error recognition; higher values will detect more errors but may
* misdetect some more or less valid parts as errors.
* Demuxing only, set by the caller before avformat_open_input().
*/
int error_recognition;
/**
* Custom interrupt callbacks for the I/O layer.
*
* demuxing: set by the user before avformat_open_input().
* muxing: set by the user before avformat_write_header()
* (mainly useful for AVFMT_NOFILE formats). The callback
* should also be passed to avio_open2() if it's used to
* open the file.
*/
AVIOInterruptCB interrupt_callback;
/**
* Flags to enable debugging.
*/
int debug;
#define FF_FDEBUG_TS 0x0001
/**
* Maximum buffering duration for interleaving.
*
* To ensure all the streams are interleaved correctly,
* av_interleaved_write_frame() will wait until it has at least one packet
* for each stream before actually writing any packets to the output file.
* When some streams are "sparse" (i.e. there are large gaps between
* successive packets), this can result in excessive buffering.
*
* This field specifies the maximum difference between the timestamps of the
* first and the last packet in the muxing queue, above which libavformat
* will output a packet regardless of whether it has queued a packet for all
* the streams.
*
* Muxing only, set by the caller before avformat_write_header().
*/
int64_t max_interleave_delta;
/**
* Allow non-standard and experimental extension
* @see AVCodecContext.strict_std_compliance
*/
int strict_std_compliance;
/**
* Flags indicating events happening on the file, a combination of
* AVFMT_EVENT_FLAG_*.
*
* - demuxing: may be set by the demuxer in avformat_open_input(),
* avformat_find_stream_info() and av_read_frame(). Flags must be cleared
* by the user once the event has been handled.
* - muxing: may be set by the user after avformat_write_header() to
* indicate a user-triggered event. The muxer will clear the flags for
* events it has handled in av_[interleaved]_write_frame().
*/
int event_flags;
/**
* - demuxing: the demuxer read new metadata from the file and updated
* AVFormatContext.metadata accordingly
* - muxing: the user updated AVFormatContext.metadata and wishes the muxer to
* write it into the file
*/
#define AVFMT_EVENT_FLAG_METADATA_UPDATED 0x0001
/**
* Maximum number of packets to read while waiting for the first timestamp.
* Decoding only.
*/
int max_ts_probe;
/**
* Avoid negative timestamps during muxing.
* Any value of the AVFMT_AVOID_NEG_TS_* constants.
* Note, this only works when using av_interleaved_write_frame. (interleave_packet_per_dts is in use)
* - muxing: Set by user
* - demuxing: unused
*/
int avoid_negative_ts;
#define AVFMT_AVOID_NEG_TS_AUTO -1 ///< Enabled when required by target format
#define AVFMT_AVOID_NEG_TS_MAKE_NON_NEGATIVE 1 ///< Shift timestamps so they are non negative
#define AVFMT_AVOID_NEG_TS_MAKE_ZERO 2 ///< Shift timestamps so that they start at 0
/**
* Transport stream id.
* This will be moved into demuxer private options. Thus no API/ABI compatibility
*/
int ts_id;
/**
* Audio preload in microseconds.
* Note, not all formats support this and unpredictable things may happen if it is used when not supported.
* - encoding: Set by user
* - decoding: unused
*/
int audio_preload;
/**
* Max chunk time in microseconds.
* Note, not all formats support this and unpredictable things may happen if it is used when not supported.
* - encoding: Set by user
* - decoding: unused
*/
int max_chunk_duration;
/**
* Max chunk size in bytes
* Note, not all formats support this and unpredictable things may happen if it is used when not supported.
* - encoding: Set by user
* - decoding: unused
*/
int max_chunk_size;
/**
* forces the use of wallclock timestamps as pts/dts of packets
* This has undefined results in the presence of B frames.
* - encoding: unused
* - decoding: Set by user
*/
int use_wallclock_as_timestamps;
/**
* avio flags, used to force AVIO_FLAG_DIRECT.
* - encoding: unused
* - decoding: Set by user
*/
int avio_flags;
/**
* The duration field can be estimated through various ways, and this field can be used
* to know how the duration was estimated.
* - encoding: unused
* - decoding: Read by user
*/
enum AVDurationEstimationMethod duration_estimation_method;
/**
* Skip initial bytes when opening stream
* - encoding: unused
* - decoding: Set by user
*/
int64_t skip_initial_bytes;
/**
* Correct single timestamp overflows
* - encoding: unused
* - decoding: Set by user
*/
unsigned int correct_ts_overflow;
/**
* Force seeking to any (also non key) frames.
* - encoding: unused
* - decoding: Set by user
*/
int seek2any;
/**
* Flush the I/O context after each packet.
* - encoding: Set by user
* - decoding: unused
*/
int flush_packets;
/**
* format probing score.
* The maximal score is AVPROBE_SCORE_MAX, its set when the demuxer probes
* the format.
* - encoding: unused
* - decoding: set by avformat, read by user
*/
int probe_score;
/**
* Maximum number of bytes read from input in order to identify the
* \ref AVInputFormat "input format". Only used when the format is not set
* explicitly by the caller.
*
* Demuxing only, set by the caller before avformat_open_input().
*
* @sa probesize
*/
int format_probesize;
/**
* ',' separated list of allowed decoders.
* If NULL then all are allowed
* - encoding: unused
* - decoding: set by user
*/
char *codec_whitelist;
/**
* ',' separated list of allowed demuxers.
* If NULL then all are allowed
* - encoding: unused
* - decoding: set by user
*/
char *format_whitelist;
/**
* IO repositioned flag.
* This is set by avformat when the underlaying IO context read pointer
* is repositioned, for example when doing byte based seeking.
* Demuxers can use the flag to detect such changes.
*/
int io_repositioned;
/**
* Forced video codec.
* This allows forcing a specific decoder, even when there are multiple with
* the same codec_id.
* Demuxing: Set by user
*/
const AVCodec *video_codec;
/**
* Forced audio codec.
* This allows forcing a specific decoder, even when there are multiple with
* the same codec_id.
* Demuxing: Set by user
*/
const AVCodec *audio_codec;
/**
* Forced subtitle codec.
* This allows forcing a specific decoder, even when there are multiple with
* the same codec_id.
* Demuxing: Set by user
*/
const AVCodec *subtitle_codec;
/**
* Forced data codec.
* This allows forcing a specific decoder, even when there are multiple with
* the same codec_id.
* Demuxing: Set by user
*/
const AVCodec *data_codec;
/**
* Number of bytes to be written as padding in a metadata header.
* Demuxing: Unused.
* Muxing: Set by user via av_format_set_metadata_header_padding.
*/
int metadata_header_padding;
/**
* User data.
* This is a place for some private data of the user.
*/
void *opaque;
/**
* Callback used by devices to communicate with application.
*/
av_format_control_message control_message_cb;
/**
* Output timestamp offset, in microseconds.
* Muxing: set by user
*/
int64_t output_ts_offset;
/**
* dump format separator.
* can be ", " or "\n " or anything else
* - muxing: Set by user.
* - demuxing: Set by user.
*/
uint8_t *dump_separator;
/**
* Forced Data codec_id.
* Demuxing: Set by user.
*/
enum AVCodecID data_codec_id;
/**
* ',' separated list of allowed protocols.
* - encoding: unused
* - decoding: set by user
*/
char *protocol_whitelist;
/**
* A callback for opening new IO streams.
*
* Whenever a muxer or a demuxer needs to open an IO stream (typically from
* avformat_open_input() for demuxers, but for certain formats can happen at
* other times as well), it will call this callback to obtain an IO context.
*
* @param s the format context
* @param pb on success, the newly opened IO context should be returned here
* @param url the url to open
* @param flags a combination of AVIO_FLAG_*
* @param options a dictionary of additional options, with the same
* semantics as in avio_open2()
* @return 0 on success, a negative AVERROR code on failure
*
* @note Certain muxers and demuxers do nesting, i.e. they open one or more
* additional internal format contexts. Thus the AVFormatContext pointer
* passed to this callback may be different from the one facing the caller.
* It will, however, have the same 'opaque' field.
*/
int (*io_open)(struct AVFormatContext *s, AVIOContext **pb, const char *url,
int flags, AVDictionary **options);
/**
* A callback for closing the streams opened with AVFormatContext.io_open().
*/
void (*io_close)(struct AVFormatContext *s, AVIOContext *pb);
/**
* ',' separated list of disallowed protocols.
* - encoding: unused
* - decoding: set by user
*/
char *protocol_blacklist;
/**
* The maximum number of streams.
* - encoding: unused
* - decoding: set by user
*/
int max_streams;
/**
* Skip duration calcuation in estimate_timings_from_pts.
* - encoding: unused
* - decoding: set by user
*/
int skip_estimate_duration_from_pts;
/**
* Maximum number of packets that can be probed
* - encoding: unused
* - decoding: set by user
*/
int max_probe_packets;
/**
* A callback for closing the streams opened with AVFormatContext.io_open().
*
* Using this is preferred over io_close, because this can return an error.
* Therefore this callback is used instead of io_close by the generic
* libavformat code if io_close is NULL or the default.
*
* @param s the format context
* @param pb IO context to be closed and freed
* @return 0 on success, a negative AVERROR code on failure
*/
int (*io_close2)(struct AVFormatContext *s, AVIOContext *pb);
} AVFormatContext;
下面的结构体就是需要插件实现的回调函数。
/**
* @addtogroup lavf_encoding
* @{
*/
typedef struct AVOutputFormat {
const char *name;
/**
* Descriptive name for the format, meant to be more human-readable
* than name. You should use the NULL_IF_CONFIG_SMALL() macro
* to define it.
*/
const char *long_name;
const char *mime_type;
const char *extensions; /**< comma-separated filename extensions */
/* output support */
enum AVCodecID audio_codec; /**< default audio codec */
enum AVCodecID video_codec; /**< default video codec */
enum AVCodecID subtitle_codec; /**< default subtitle codec */
/**
* can use flags: AVFMT_NOFILE, AVFMT_NEEDNUMBER,
* AVFMT_GLOBALHEADER, AVFMT_NOTIMESTAMPS, AVFMT_VARIABLE_FPS,
* AVFMT_NODIMENSIONS, AVFMT_NOSTREAMS, AVFMT_ALLOW_FLUSH,
* AVFMT_TS_NONSTRICT, AVFMT_TS_NEGATIVE
*/
int flags;
/**
* List of supported codec_id-codec_tag pairs, ordered by "better
* choice first". The arrays are all terminated by AV_CODEC_ID_NONE.
*/
const struct AVCodecTag * const *codec_tag;
const AVClass *priv_class; ///< AVClass for the private context
/*****************************************************************
* No fields below this line are part of the public API. They
* may not be used outside of libavformat and can be changed and
* removed at will.
* New public fields should be added right above.
*****************************************************************
*/
/**
* size of private data so that it can be allocated in the wrapper
*/
int priv_data_size;
/**
* Internal flags. See FF_FMT_FLAG_* in internal.h.
*/
int flags_internal;
int (*write_header)(struct AVFormatContext *);
/**
* Write a packet. If AVFMT_ALLOW_FLUSH is set in flags,
* pkt can be NULL in order to flush data buffered in the muxer.
* When flushing, return 0 if there still is more data to flush,
* or 1 if everything was flushed and there is no more buffered
* data.
*/
int (*write_packet)(struct AVFormatContext *, AVPacket *pkt);
int (*write_trailer)(struct AVFormatContext *);
/**
* A format-specific function for interleavement.
* If unset, packets will be interleaved by dts.
*
* @param s An AVFormatContext for output. pkt will be added to
* resp. taken from its packet buffer.
* @param[in,out] pkt A packet to be interleaved if has_packet is set;
* also used to return packets. If no packet is returned
* (e.g. on error), pkt is blank on return.
* @param flush 1 if no further packets are available as input and
* all remaining packets should be output.
* @param has_packet If set, pkt contains a packet to be interleaved
* on input; otherwise pkt is blank on input.
* @return 1 if a packet was output, 0 if no packet could be output,
* < 0 if an error occurred
*/
int (*interleave_packet)(struct AVFormatContext *s, AVPacket *pkt,
int flush, int has_packet);
/**
* Test if the given codec can be stored in this container.
*
* @return 1 if the codec is supported, 0 if it is not.
* A negative number if unknown.
* MKTAG('A', 'P', 'I', 'C') if the codec is only supported as AV_DISPOSITION_ATTACHED_PIC
*/
int (*query_codec)(enum AVCodecID id, int std_compliance);
void (*get_output_timestamp)(struct AVFormatContext *s, int stream,
int64_t *dts, int64_t *wall);
/**
* Allows sending messages from application to device.
*/
int (*control_message)(struct AVFormatContext *s, int type,
void *data, size_t data_size);
/**
* Write an uncoded AVFrame.
*
* See av_write_uncoded_frame() for details.
*
* The library will free *frame afterwards, but the muxer can prevent it
* by setting the pointer to NULL.
*/
int (*write_uncoded_frame)(struct AVFormatContext *, int stream_index,
AVFrame **frame, unsigned flags);
/**
* Returns device list with it properties.
* @see avdevice_list_devices() for more details.
*/
int (*get_device_list)(struct AVFormatContext *s, struct AVDeviceInfoList *device_list);
enum AVCodecID data_codec; /**< default data codec */
/**
* Initialize format. May allocate data here, and set any AVFormatContext or
* AVStream parameters that need to be set before packets are sent.
* This method must not write output.
*
* Return 0 if streams were fully configured, 1 if not, negative AVERROR on failure
*
* Any allocations made here must be freed in deinit().
*/
int (*init)(struct AVFormatContext *);
/**
* Deinitialize format. If present, this is called whenever the muxer is being
* destroyed, regardless of whether or not the header has been written.
*
* If a trailer is being written, this is called after write_trailer().
*
* This is called if init() fails as well.
*/
void (*deinit)(struct AVFormatContext *);
/**
* Set up any necessary bitstream filtering and extract any extra data needed
* for the global header.
*
* @note pkt might have been directly forwarded by a meta-muxer; therefore
* pkt->stream_index as well as the pkt's timebase might be invalid.
* Return 0 if more packets from this stream must be checked; 1 if not.
*/
int (*check_bitstream)(struct AVFormatContext *s, struct AVStream *st,
const AVPacket *pkt);
} AVOutputFormat;
操作函数
/**
* Allocate an AVFormatContext.
* avformat_free_context() can be used to free the context and everything
* allocated by the framework within it.
*/
AVFormatContext *avformat_alloc_context(void);
/**
* Free an AVFormatContext and all its streams.
* @param s context to free
*/
void avformat_free_context(AVFormatContext *s);
/**
* Add a new stream to a media file.
*
* When demuxing, it is called by the demuxer in read_header(). If the
* flag AVFMTCTX_NOHEADER is set in s.ctx_flags, then it may also
* be called in read_packet().
*
* When muxing, should be called by the user before avformat_write_header().
*
* User is required to call avformat_free_context() to clean up the allocation
* by avformat_new_stream().
*
* @param s media file handle
* @param c unused, does nothing
*
* @return newly created stream or NULL on error.
*/
AVStream *avformat_new_stream(AVFormatContext *s, const AVCodec *c);
/**
* Wrap an existing array as stream side data.
*
* @param st stream
* @param type side information type
* @param data the side data array. It must be allocated with the av_malloc()
* family of functions. The ownership of the data is transferred to
* st.
* @param size side information size
* @return zero on success, a negative AVERROR code on failure. On failure,
* the stream is unchanged and the data remains owned by the caller.
*/
int av_stream_add_side_data(AVStream *st, enum AVPacketSideDataType type,
uint8_t *data, size_t size);
/**
* Allocate new information from stream.
*
* @param stream stream
* @param type desired side information type
* @param size side information size
* @return pointer to fresh allocated data or NULL otherwise
*/
uint8_t *av_stream_new_side_data(AVStream *stream,
enum AVPacketSideDataType type, size_t size);
/**
* Get side information from stream.
*
* @param stream stream
* @param type desired side information type
* @param size If supplied, *size will be set to the size of the side data
* or to zero if the desired side data is not present.
* @return pointer to data if present or NULL otherwise
*/
uint8_t *av_stream_get_side_data(const AVStream *stream,
enum AVPacketSideDataType type, size_t *size);
/**
* Allocate an AVFormatContext for an output format.
* avformat_free_context() can be used to free the context and
* everything allocated by the framework within it.
*
* @param *ctx is set to the created format context, or to NULL in
* case of failure
* @param oformat format to use for allocating the context, if NULL
* format_name and filename are used instead
* @param format_name the name of output format to use for allocating the
* context, if NULL filename is used instead
* @param filename the name of the filename to use for allocating the
* context, may be NULL
* @return >= 0 in case of success, a negative AVERROR code in case of
* failure
*/
int avformat_alloc_output_context2(AVFormatContext **ctx, const AVOutputFormat *oformat,
const char *format_name, const char *filename);
/**
* @addtogroup lavf_decoding
* @{
*/
/**
* Find AVInputFormat based on the short name of the input format.
*/
const AVInputFormat *av_find_input_format(const char *short_name);
/**
* Guess the file format.
*
* @param pd data to be probed
* @param is_opened Whether the file is already opened; determines whether
* demuxers with or without AVFMT_NOFILE are probed.
*/
const AVInputFormat *av_probe_input_format(const AVProbeData *pd, int is_opened);
/**
* Guess the file format.
*
* @param pd data to be probed
* @param is_opened Whether the file is already opened; determines whether
* demuxers with or without AVFMT_NOFILE are probed.
* @param score_max A probe score larger that this is required to accept a
* detection, the variable is set to the actual detection
* score afterwards.
* If the score is <= AVPROBE_SCORE_MAX / 4 it is recommended
* to retry with a larger probe buffer.
*/
const AVInputFormat *av_probe_input_format2(const AVProbeData *pd,
int is_opened, int *score_max);
/**
* Guess the file format.
*
* @param is_opened Whether the file is already opened; determines whether
* demuxers with or without AVFMT_NOFILE are probed.
* @param score_ret The score of the best detection.
*/
const AVInputFormat *av_probe_input_format3(const AVProbeData *pd,
int is_opened, int *score_ret);
/**
* Probe a bytestream to determine the input format. Each time a probe returns
* with a score that is too low, the probe buffer size is increased and another
* attempt is made. When the maximum probe size is reached, the input format
* with the highest score is returned.
*
* @param pb the bytestream to probe
* @param fmt the input format is put here
* @param url the url of the stream
* @param logctx the log context
* @param offset the offset within the bytestream to probe from
* @param max_probe_size the maximum probe buffer size (zero for default)
* @return the score in case of success, a negative value corresponding to an
* the maximal score is AVPROBE_SCORE_MAX
* AVERROR code otherwise
*/
int av_probe_input_buffer2(AVIOContext *pb, const AVInputFormat **fmt,
const char *url, void *logctx,
unsigned int offset, unsigned int max_probe_size);
/**
* Like av_probe_input_buffer2() but returns 0 on success
*/
int av_probe_input_buffer(AVIOContext *pb, const AVInputFormat **fmt,
const char *url, void *logctx,
unsigned int offset, unsigned int max_probe_size);
/**
* Open an input stream and read the header. The codecs are not opened.
* The stream must be closed with avformat_close_input().
*
* @param ps Pointer to user-supplied AVFormatContext (allocated by avformat_alloc_context).
* May be a pointer to NULL, in which case an AVFormatContext is allocated by this
* function and written into ps.
* Note that a user-supplied AVFormatContext will be freed on failure.
* @param url URL of the stream to open.
* @param fmt If non-NULL, this parameter forces a specific input format.
* Otherwise the format is autodetected.
* @param options A dictionary filled with AVFormatContext and demuxer-private options.
* On return this parameter will be destroyed and replaced with a dict containing
* options that were not found. May be NULL.
*
* @return 0 on success, a negative AVERROR on failure.
*
* @note If you want to use custom IO, preallocate the format context and set its pb field.
*/
int avformat_open_input(AVFormatContext **ps, const char *url,
const AVInputFormat *fmt, AVDictionary **options);
/**
* Read packets of a media file to get stream information. This
* is useful for file formats with no headers such as MPEG. This
* function also computes the real framerate in case of MPEG-2 repeat
* frame mode.
* The logical file position is not changed by this function;
* examined packets may be buffered for later processing.
*
* @param ic media file handle
* @param options If non-NULL, an ic.nb_streams long array of pointers to
* dictionaries, where i-th member contains options for
* codec corresponding to i-th stream.
* On return each dictionary will be filled with options that were not found.
* @return >=0 if OK, AVERROR_xxx on error
*
* @note this function isn't guaranteed to open all the codecs, so
* options being non-empty at return is a perfectly normal behavior.
*
* @todo Let the user decide somehow what information is needed so that
* we do not waste time getting stuff the user does not need.
*/
int avformat_find_stream_info(AVFormatContext *ic, AVDictionary **options);
/**
* Find the programs which belong to a given stream.
*
* @param ic media file handle
* @param last the last found program, the search will start after this
* program, or from the beginning if it is NULL
* @param s stream index
* @return the next program which belongs to s, NULL if no program is found or
* the last program is not among the programs of ic.
*/
AVProgram *av_find_program_from_stream(AVFormatContext *ic, AVProgram *last, int s);
void av_program_add_stream_index(AVFormatContext *ac, int progid, unsigned int idx);
/**
* Find the "best" stream in the file.
* The best stream is determined according to various heuristics as the most
* likely to be what the user expects.
* If the decoder parameter is non-NULL, av_find_best_stream will find the
* default decoder for the stream's codec; streams for which no decoder can
* be found are ignored.
*
* @param ic media file handle
* @param type stream type: video, audio, subtitles, etc.
* @param wanted_stream_nb user-requested stream number,
* or -1 for automatic selection
* @param related_stream try to find a stream related (eg. in the same
* program) to this one, or -1 if none
* @param decoder_ret if non-NULL, returns the decoder for the
* selected stream
* @param flags flags; none are currently defined
* @return the non-negative stream number in case of success,
* AVERROR_STREAM_NOT_FOUND if no stream with the requested type
* could be found,
* AVERROR_DECODER_NOT_FOUND if streams were found but no decoder
* @note If av_find_best_stream returns successfully and decoder_ret is not
* NULL, then *decoder_ret is guaranteed to be set to a valid AVCodec.
*/
int av_find_best_stream(AVFormatContext *ic,
enum AVMediaType type,
int wanted_stream_nb,
int related_stream,
const AVCodec **decoder_ret,
int flags);
其实想要说明的一些函数是下面的,这些函数可以用来控制输入流的播放,暂停,跳转,等,特别是在rtsp等流媒体服务器上,非常有用。
就这些吧,等到后面分析rtsp和rtmp的客户端的时候,我们再来详细的讲一下这些函数的调用流程,今天就先列出来吧。
/**
* Return the next frame of a stream.
* This function returns what is stored in the file, and does not validate
* that what is there are valid frames for the decoder. It will split what is
* stored in the file into frames and return one for each call. It will not
* omit invalid data between valid frames so as to give the decoder the maximum
* information possible for decoding.
*
* On success, the returned packet is reference-counted (pkt->buf is set) and
* valid indefinitely. The packet must be freed with av_packet_unref() when
* it is no longer needed. For video, the packet contains exactly one frame.
* For audio, it contains an integer number of frames if each frame has
* a known fixed size (e.g. PCM or ADPCM data). If the audio frames have
* a variable size (e.g. MPEG audio), then it contains one frame.
*
* pkt->pts, pkt->dts and pkt->duration are always set to correct
* values in AVStream.time_base units (and guessed if the format cannot
* provide them). pkt->pts can be AV_NOPTS_VALUE if the video format
* has B-frames, so it is better to rely on pkt->dts if you do not
* decompress the payload.
*
* @return 0 if OK, < 0 on error or end of file. On error, pkt will be blank
* (as if it came from av_packet_alloc()).
*
* @note pkt will be initialized, so it may be uninitialized, but it must not
* contain data that needs to be freed.
*/
int av_read_frame(AVFormatContext *s, AVPacket *pkt);
/**
* Seek to the keyframe at timestamp.
* 'timestamp' in 'stream_index'.
*
* @param s media file handle
* @param stream_index If stream_index is (-1), a default
* stream is selected, and timestamp is automatically converted
* from AV_TIME_BASE units to the stream specific time_base.
* @param timestamp Timestamp in AVStream.time_base units
* or, if no stream is specified, in AV_TIME_BASE units.
* @param flags flags which select direction and seeking mode
* @return >= 0 on success
*/
int av_seek_frame(AVFormatContext *s, int stream_index, int64_t timestamp,
int flags);
/**
* Seek to timestamp ts.
* Seeking will be done so that the point from which all active streams
* can be presented successfully will be closest to ts and within min/max_ts.
* Active streams are all streams that have AVStream.discard < AVDISCARD_ALL.
*
* If flags contain AVSEEK_FLAG_BYTE, then all timestamps are in bytes and
* are the file position (this may not be supported by all demuxers).
* If flags contain AVSEEK_FLAG_FRAME, then all timestamps are in frames
* in the stream with stream_index (this may not be supported by all demuxers).
* Otherwise all timestamps are in units of the stream selected by stream_index
* or if stream_index is -1, in AV_TIME_BASE units.
* If flags contain AVSEEK_FLAG_ANY, then non-keyframes are treated as
* keyframes (this may not be supported by all demuxers).
* If flags contain AVSEEK_FLAG_BACKWARD, it is ignored.
*
* @param s media file handle
* @param stream_index index of the stream which is used as time base reference
* @param min_ts smallest acceptable timestamp
* @param ts target timestamp
* @param max_ts largest acceptable timestamp
* @param flags flags
* @return >=0 on success, error code otherwise
*
* @note This is part of the new seek API which is still under construction.
*/
int avformat_seek_file(AVFormatContext *s, int stream_index, int64_t min_ts, int64_t ts, int64_t max_ts, int flags);
/**
* Discard all internally buffered data. This can be useful when dealing with
* discontinuities in the byte stream. Generally works only with formats that
* can resync. This includes headerless formats like MPEG-TS/TS but should also
* work with NUT, Ogg and in a limited way AVI for example.
*
* The set of streams, the detected duration, stream parameters and codecs do
* not change when calling this function. If you want a complete reset, it's
* better to open a new AVFormatContext.
*
* This does not flush the AVIOContext (s->pb). If necessary, call
* avio_flush(s->pb) before calling this function.
*
* @param s media file handle
* @return >=0 on success, error code otherwise
*/
int avformat_flush(AVFormatContext *s);
/**
* Start playing a network-based stream (e.g. RTSP stream) at the
* current position.
*/
int av_read_play(AVFormatContext *s);
/**
* Pause a network-based stream (e.g. RTSP stream).
*
* Use av_read_play() to resume it.
*/
int av_read_pause(AVFormatContext *s);
/**
* Close an opened input AVFormatContext. Free it and all its contents
* and set *s to NULL.
*/
void avformat_close_input(AVFormatContext **s);
/**
* @}
*/